银行卡识别
环境
Python3.6
opencv-python 3.4.1.15
1
pip install opencv-python==3.4.1.15
opencv-contrib-python 3.4.1.15
1
pip install opencv-contrib-python==3.4.1.15
matplotlib
1 | #引用 |
常用函数
1 | cv2.imread(src) #读取图片 |
图像阈值
1 | ret,dst = cv2.threshold(src,thresh,maxval,type) |
平滑处理
1 | #均值滤波 |
形态学
1 | #核 |
图像梯度 - Sobel算子
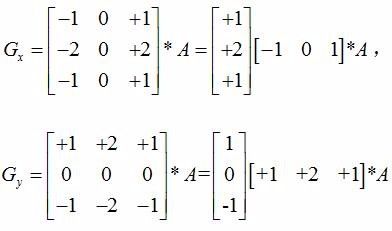
1 | sobelx = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64,1,0,ksize = size) |
图像梯度 - Scharr算子
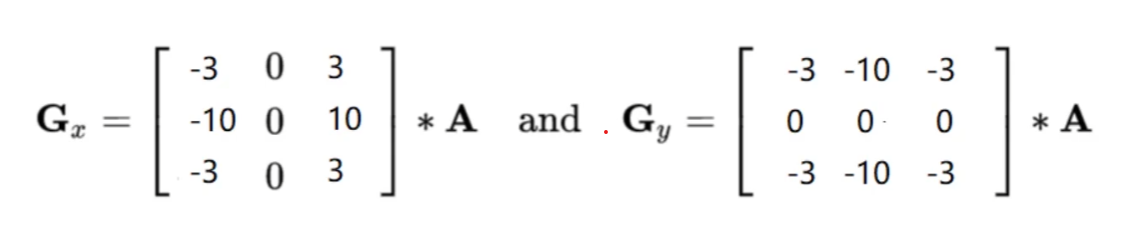
1 | scharrx = cv2.Scharr(img,cv2.CV_64,1,0,ksize = size) |
图像梯度 - laplacian算子
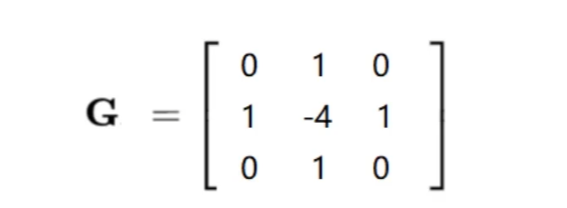
1 | laplacian = cv2.Laplacian(img,cv2.CV_64F) |
Canny边缘检测
- 使用高斯滤波器,以平滑图像,滤除噪声
- 计算图像中每个像素点的梯度强度和方向
- 应用非极大值(Non-Maximum Suppression)抑制,以消除边缘检测带来的杂散相应
- 应用双阈值(Double-Threshold)检测来确定真实的和潜在的边缘
- 通过抑制孤立的弱边缘最终来完成边缘检测
高斯滤波器
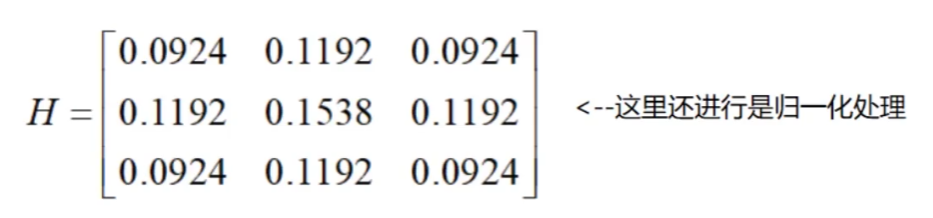
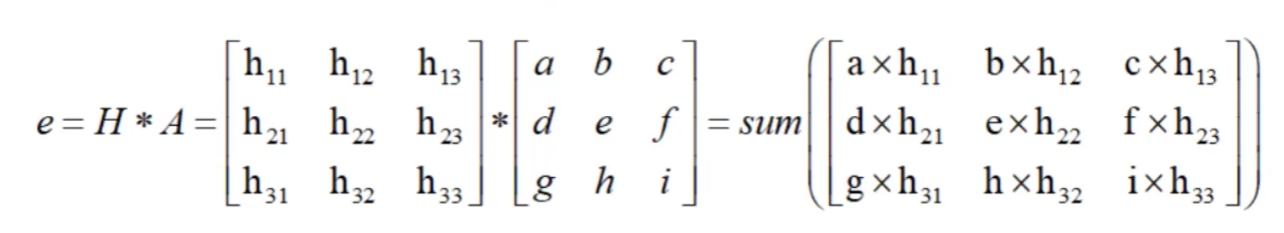
梯度和方向
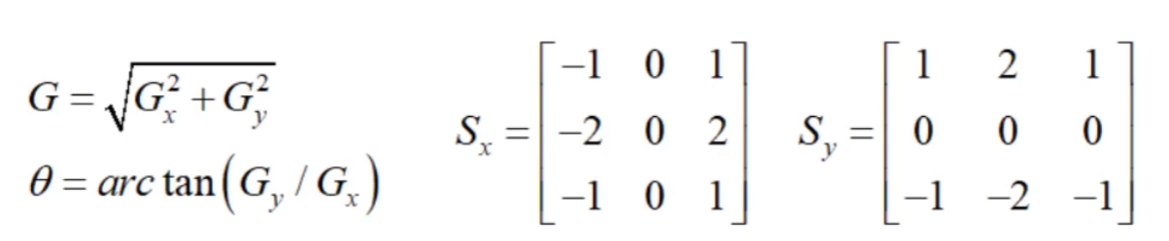
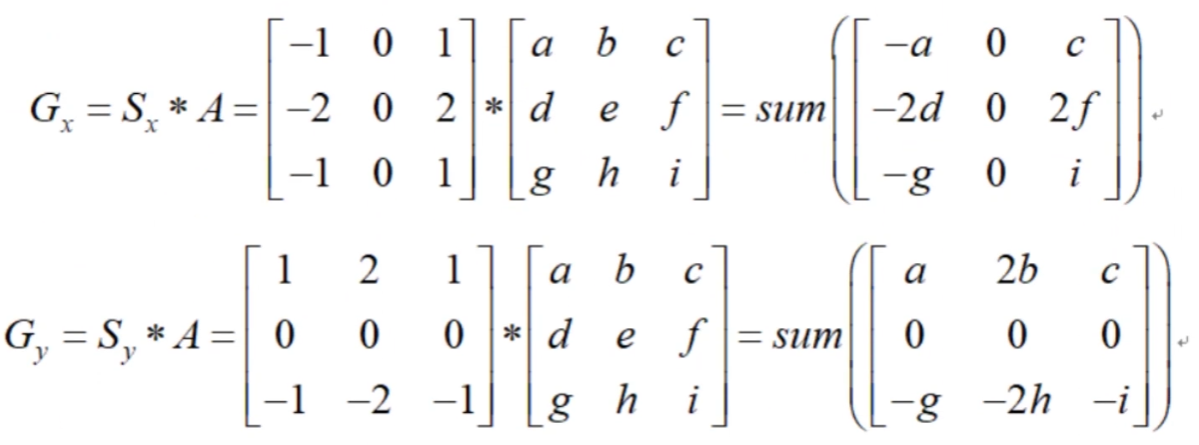
非极大值抑制
双阈值检测

openCV中Canny算子的使用
1 | result = cv2.Canny(img,minVal,maxVal) |
图像金字塔
高斯金字塔
向下采样方法(缩小)
- 将图像与高斯内核卷积
- 将所有偶数行和列去除
1 | down = cv2.pyrDown(img) |
向上采样方法(放大)
- 将图像在每个方向扩大为原来的两倍,新增的行和列以0填充
- 使用先前同样的内核(乘以4)与放大后的图像卷积,获得近似值
1 | up = cv2.pyrUp(img) |
拉普拉斯金字塔
轮廓检测
轮廓检测函数
findContours
1 | binary, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img,mode,method) |
drawContours
1 | cv2.drawContours(img, contours, contourIdx, color[, thickness[, lineType[, hierarchy[, maxLevel[, offset ]]]]]) |
识别结果
轮廓特征
1 | cv2.contourArea(cnt) #面积 |
轮廓近似
1 | # 定义一个近似阈值 例如 standard = 0.1 * cv2.arcLength(cnt,Ture) |
边界矩形
1 | x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) |
外接圆
1 | (x,y),radius = cv.minEnclosingCircle(cnt) |
模板匹配
1 | res = cv2.matchTemplate(img,template,Method) |
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
template = cv2.imread('./img/girl.png')
h,w = template.shape[:2]
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img, template, cv2.TM_SQDIFF)
min_val,max_val,min_loc,max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
img_copy = img.copy()
res = cv2.rectangle(img_copy,min_loc,(min_loc[0]+w,min_loc[1]+h),(0,0,255),2)
cv_show("res",res)
银行卡识别
1 | import cv2 |
实验用的银行卡
获取银行卡数字轮廓
识别结果
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来源 还(huan)!